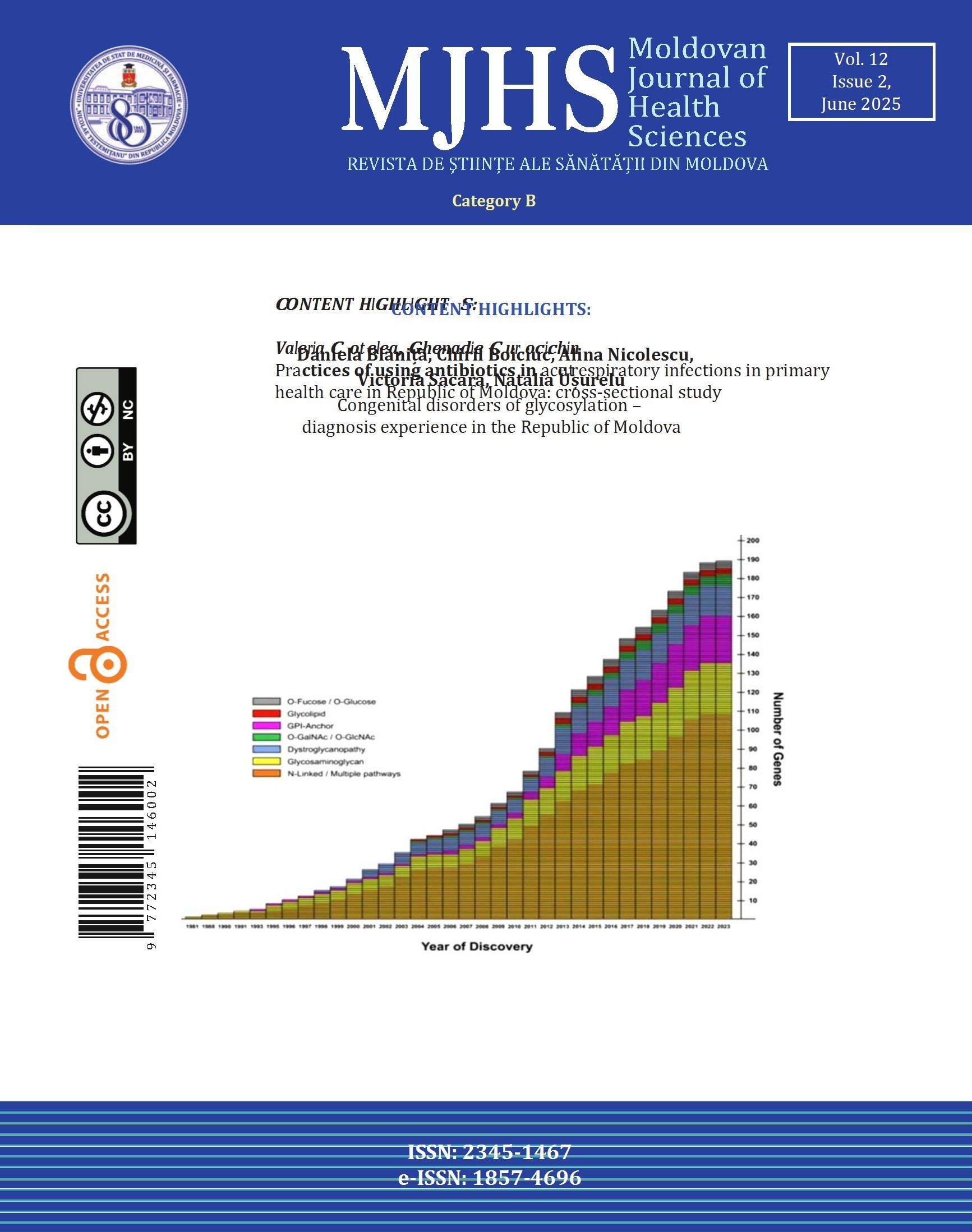
Congenital disorders of glycosylation (CDG) represent a group of rare diseases with multisystem involvement and exponential expansion, characterized by defects in the glycosylation process, which is essential for the proper functioning of proteins and lipids. These often manifest under the guise of other pathologies. The objective of the study was to diagnose CDG using Isoelectric Focusing of Transferrin (IEFT) in the Republic of Moldova and to identify diseases that mimic CDG.
Current issue
Volume
12.
Issue
2
June, 2025
most recent article
„Health status of employees in meat processing enterprises and preventive measures” Authors: Iurie Pînzaru, Grigore Friptuleac, Agripina Rașcu
Monograph details:
Pînzaru I, Friptuleac G, Rașcu A. Starea de sănătate a angajaților întreprinderilotr de procesare a cărnii și măsurile de profilaxie [Health status of employees in meat processing enterprises and preventive measures]. Chișinău; 2024. 259 p. ISBN 978-9975-57-369-6. Romanian.
Recent articles
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma is a heterogeneous group of malignant lymphoid tumors. Hemostasis disorders in non-Hodgkin lymphoma are often asymptomatic but can develop into severe complications. The risk of venous thromboembolism increases according to the totality of risk factors assessed directly in each individual patient, based on age, gender, comorbidities, performance status, and both congenital and acquired thrombophilia
Neuropsychiatric lupus erythematosus is still a disease with a very challenging diagnostic process, lacking high specificity and sensitivity assays. Autoantibodies can change this perspective, and because of their pathogenetic involvement, can become a very powerful tool for early detection and disease activity tracking. However, their biomarker potential still needs further evaluation. In this study, we focused on the pathogenetic mechanisms of neuropsychiatric lupus erythematosus and the involvement of brain-specific and systemic autoantibodies in the development of neuropsychiatric manifestations.
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a major and growing global public health problem, contributing to significant morbidity, mortality, and financial strain on healthcare systems. Despite available preventive measures, CKD often remains underdiagnosed and insufficiently addressed by health policies worldwide.
Scleroderma Renal Crisis (SRC) is a life-threatening complication of systemic sclerosis (SSc), traditionally associated with anti-RNA polymerase III antibodies, corticosteroid use, and diffuse skin involvement. However, the role of COVID-19 as a potential trigger for SRC remains poorly understood. This study explores the occurrence of COVID-19-associated SRC, focusing on its clinical presentation, underlying risk factors, and outcomes