Introduction
Drug addiction is one of today's most serious social issues, and it has recently become a global pandemic. In the Republic of Moldova, this problem is very pronounced. This is due to many factors, the main one being easy accessibility. Consumption of cheap and low-quality drugs leads to necrosis of the jaws and, with prolonged use, to the destruction of all facial bones.
One of the important methods of diagnosing atypical osteomyelitis of the jaw bones is taking a thorough history. From the words of the patients, it was concluded that this disease appeared after the use of a substance called amphetamine. Besides the basic substance, which is ephedrine, this stuff contains other substances, such as red phosphorus and iodine, which lead to trophic changes when they accumulate in the tissues. Through its action, ephedrine leads to long-term vascular spasm that induces angiopathy [1].
A review of data from the modern literature as well as clinical cases of patients with jaw necrosis in recent years has shown that there are several narcotic drugs that lead to destruction of jaw bone tissue. Specialized treatment in the oromaxillofacial surgery department of patients with toxic osteomyelitis is difficult and tedious, with a number of impediments on the part of patients, who usually do not notice the seriousness of the problem. After the condition has improved, most of them continue to take drugs, abandoning their prescriptions, and end up with even more severe complications. Patients with toxic osteomyelitis of the jaw who do not attend regular check-ups cause a slew of medical and social issues [2].
The relevance of the problem lies in the detection of the causes of the development of this pathology, diagnostic methods and, most importantly, the development of effective treatment methods.
Osteomyelitis of the upper jaw is accompanied by such complications as abscesses or phlegmon of regional soft tissues, purulent sinusitis, frontitis, and ethmoiditis. Severe complications include meningitis and septicemia.
According to patients, another drug (abbreviated α-PVP, from English α-pyrrolidinovalerophenone) appeared in Moldova in 2021 – a synthetic cathinone psychostimulant that also causes necrosis of the facial bones [3].
Toxic osteomyelitis of the facial bones occurs not only in the Republic of Moldova but also in its neighboring countries – the Russian Federation and Ukraine. This pathology occurs because of the use of the drug amphetamine, which is cheap and accessible to synthesize under clandestine conditions. This drug contains ephedrine, red phosphorus, and iodine [4-7].
Material and methods
Clinical cases of male and female patients aged 25–55 years with jaw necrosis associated with narcotic use (history, results of paraclinical research methods), and data from modern literature were studied.
The study has been conducted in the oro-maxillo-facial surgery department of the Institute of Emergency Medicine since 2005. All patients were drug users (ephedrine, red phosphorus, iodine compounds, and other chemicals, and, more recently, synthetic psychostimulants of the α-PVP cathinone class).
The following parameters were studied: social integration, whether they continue to use drugs, functional disorders (mastication, swallowing, phonation, breathing), aesthetic disorders (asymmetry, scars, aesthetic appearance), morphological disorders (lack of bone continuity, lack of teeth, oro-sinus communication, bone exposure).
The examination methods at the control visits were classical clinical examination of the patient; radiological examination (OPG, CBCT); laboratory examinations (general and biochemical blood analysis, urine analysis). Additionally, patients were documented through photography. All patients in the study signed informed consents for the examination and performance of medical procedures as well as the use of personal data for scientific and didactic purposes and the monitoring of disease progression over time.
Results
Based on the data studied, it was revealed that there are several types of narcotics that lead to jaw necrosis. It was previously noted that these changes are caused by an amphetamine drug (containing ephedrine, iodine, and red phosphorus). Another drug (abbreviated α-PVP, from English α-pyrrolidinovalerophenone), a synthetic psychostimulant of the cathinone class, appeared in Moldova in 2021, according to patient reports. The central nervous system is stimulated after taking α-PVP due to increased dopamine and norepinephrine production and release in the brain. The common thing in these preparations is the red phosphorus content; only in the latter preparation does bone destruction occur much faster.
Clinical case
T. A., a 42-year-old man, has been using amphetamines for over 15 years. In this case, there was a necrotized chin region and mandible body on the left. He was repeatedly admitted with abscesses and phlegmon in the cervicofacial region. The necrotic fragments of the mandible were removed by the sequesters over a period of 4 years, resulting in a bone and soft tissue defect.
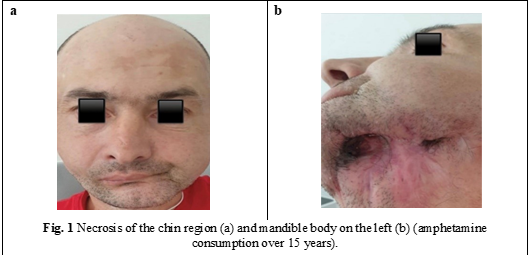
Through the defect of the buccal plateau, saliva is removed from the oral cavity (Fig. 1), leading to functional disorders (mastication, swallowing, and phonation), aesthetic disorders (facial asymmetry, presence of scars in the submandibular region), and morphological disorders (lack of bone continuity, lack of teeth). Placement of the defect with surrounding soft tissues was performed. As a result of being treated at home for synesthesia, most patients present to us with a variety of complications, including deforming scars, massive defects, pronounced facial asymmetry, and functional disorders.
D. K., a 50-year-old man. In the anamnesis, he presents long-term consumption of an amphetamine drug; at present, he is using Methadone.
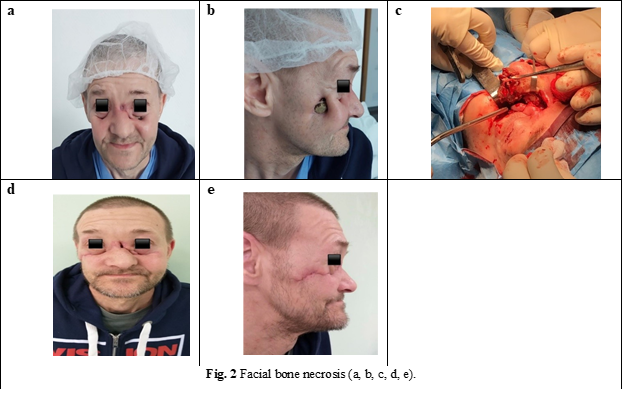
The entire upper jaw was necrotic, with damage to the maxillary sinuses and zygomatic bones and damage to the orbital plane and nasal bones (Fig. 2). After stopping amphetamine drug administration, the portions affected by necrosis (alveolar process with teeth, the hard palate entirely, and the zygomatic and nasal bones) were removed. Radical cure of the maxillary sinuses was performed without placement of the communications. Due to the chronic inflammatory process of the mucosa, dehiscences of the operative wound were formed, and as a result, repeated oro-sinus communications, functional disorders (mastication, phonation), and morphological disorders occurred. In view of what has been reported, it is very important that patients with toxic osteomyelitis of the jaws be treated simultaneously by several specialists, namely the oro-maxillofacial surgeon, psychologist, narcologist, and therapist. Equally important for their psycho-emotional, morpho-functional, and aesthetic rehabilitation is their referral for check-ups and multiple, sometimes quite complicated and lengthy surgeries.
D. B., a 33-year-old man, has a medical history of amphetamine use and has recently used α-PVP.
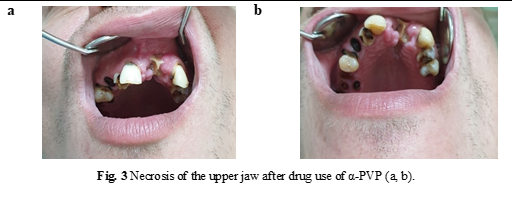
The frontal part of the upper jaw was necrotized, i.e., the part where the drugging took place by friction of the preparation in the mucosa of the nostril was more pronouncedly affected (Fig. 3). This patient is undergoing rehabilitation in a narcology clinic and is preparing for surgical treatment.
Discussions
The study of the composition of used substances is an important factor in the definition and development of the given disease's cause and mechanism. According to the patient's account, this disease appeared after the use of the drug amphetamine. This drug contained the main substance, ephedrine, and also red phosphorus and iodine, which accumulate and cause trophic changes. Almost all organisms' systems are affected by amphetamine intoxication. Given that only surgical treatment has any effect on any of the patients in this group, we devised a conservative presurgical treatment plan. Lavages of the mouth cavity are performed on a daily basis, and necrectomy is eventually performed. The elaborated scheme of conservative and surgical treatment yielded positive results in the treatment of toxic jaw osteomyelitis.
Conclusions
1. Based on the data from the literature studied as well as the clinical data, it can be concluded that jaw necrosis occurs against the background of various narcotic drugs containing red phosphorus, as this specific chemical component leads to necrosis of the facial bones.
2. Analyzing over the years the clinical and paraclinical data of patients with toxic osteomyelitis of the jaws, we can state that positive results of treatment were obtained only in patients who totally refused drug use, overcame drug dependence, and had the desire to recover.
3. When amphetamine and α-PVP users are compared, it can be concluded that α-PVP causes more rapid and extensive irreversible processes in the jaws and other facial bones.
Competing interests
None declared
Patient consent
Obtained
Author’s ORCID ID
Natalia Rusu-Radzichevici, https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1762-8403
References
1. Radzichevici M, Rusu-Radzichevici N, Şcerbatiuc D, Chele N. Osteomielita toxică a maxilarului inferior la pacienţii consumatori de droguri. Nr.435. Protocol clinic national, 2017-06-06, 28p.
2. Rusu-Radzichevici N, Radzichevici M, Şcerbatiuc D, Chele N. Osteomielita toxică a maxilarului superior la pacienţii consumatori de droguri. Nr.436. Protocol clinic national. 2017- 06-06, 28p.
3. Sauer S, Peters F. T., Haas C., Meyer M. R., Fritschi G., Maurer H.H. New designer drug α-pyrrolidinovalerophenone (PVP): studies on its metabolism and toxicological detection in rat urine using gas chromatographic/mass spectrometric techniques. J. Mass Spectrom., 2009; 44: p.952-964. doi: 10.1002/jms.1571.
4. Басин ЕМ, Медведев ЮА. Принципы лечения остеонекрозов верхней челюсти у лиц с наркотической зависимостью. Тихоокеанский медицинский журнал, 2013;(1):87-89.
5. Медведев ЮА, Басин ЕМ. Фосфорные некрозы челюстей. Врач 2012; (1):21-25.
6. Тимофеев АА, Дакал АВ. Особенности клинической симптоматики остеомиелитов челюстей у наркоманов. XVI Международная конференция челюстно-лицевых хирургов «Новые технологии в стоматологии». СПб., 2011; 177-178.
7. Уракова ЕВ, Нестеров ОВ. Выбор методов оперативного лечения больных с дезоморфиновым остеомиелитом. Практическая медицина 04 (14), инновационные технологии в медицине. Том 2, Хирургия, 2014; c.24.

