Introduction
Endoosseous dental implants are a reliable method for rehabilitating edentulous areas. The Branemark protocol, a standard insertion method, involves delayed loading after a 4–6-month osseointegration period [1]. High patient demands for faster and aesthetically superior outcomes have led to the development of immediate loading protocols.
Immediate loading offers faster aesthetic and functional results. According to studies, immediate loading prostheses have success rates ranging from 94% to 98%. Such outcomes depend heavily on patient-specific factors such as bone density, oral hygiene, and professional expertise [1-4].
The need for immediate aesthetic restoration is particularly critical in anterior zones. Research has shown that atraumatic extraction techniques preserve the alveolar ridge, minimizing bone resorption and supporting gingival contour stability. Proper implant positioning and achieving primary stability with torque values exceeding 35 Ncm are critical to avoiding micromovements that could jeopardize osseointegration [5, 6].
Additionally, the type of provisional restoration used plays a significant role in preserving the gingival architecture and ensuring occlusal harmony. Biomechanical studies emphasize the importance of limiting occlusal forces during the healing period to avoid complications. This study demonstrates the effectiveness of immediate post-extraction implantation and loading, supported by atraumatic extraction techniques and precise implant placement, ensuring both functional and aesthetic outcomes [5, 7-9].
Clinical case presentation
A 47-year-old patient presented with compromised teeth (11 and 13). Clinical examination revealed a mobile metal-ceramic bridge with vestibulo-oral mobility and sensitivity upon palpation and percussion. Radiographic analysis confirmed periapical pathology and significant bone loss, necessitating extraction (Fig. 1). Patient consent was obtained, and all procedures adhered to ethical guidelines.
Procedure
Atraumatic extraction of teeth 11 and 13 was performed to preserve the alveolar ridge. The post-extraction sockets were thoroughly curetted to remove pathological tissue and irrigated with antiseptic solutions (Fig. 2a).
Immediate post-extraction implants (diameter: 4 mm, lengths: 12 mm and 14 mm) were placed. The insertion axis was palatalized to ensure optimal engagement with cortical bone (Fig. 2b).
Under-drilling protocols were employed to enhance primary stability. The integrity of alveolar walls was carefully evaluated, with particular attention to the vestibular plate.
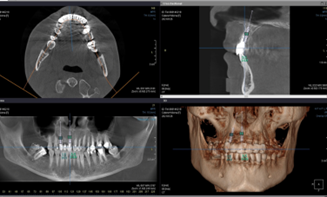 |  |
Fig. 1 Preoperative appearance. A. Tomography analysis, and digital surgery planning. B. Intraoral aspect of the prosthetic work. | |
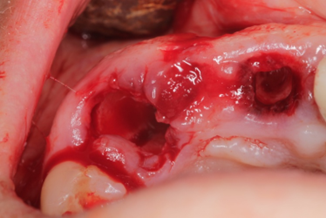 | 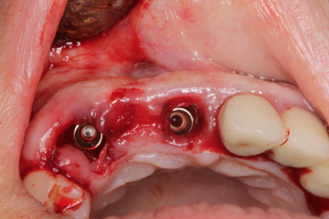 |
Fig. 2 Post-extraction socket. A. Evaluation of post-extraction socket, and bone wall integrity B. Implant placement palatal, for better soft tissue result | |
Measurements
Implant stability was assessed using a torque wrench, with insertion forces measured at 50 Ncm.
Periotestometry was performed, yielding values of -5 (mesial implant) and -6 (distal implant), indicative of excellent primary stability.
Restoration
Provisional acrylic crowns were fabricated and loaded within 48 hours. These restorations were designed to avoid occlusal contact during mastication, preventing undue stress on the implants (Fig. 3b).
Soft tissue modeling was facilitated by the provisional crowns, ensuring optimal gingival contour preservation (Fig. 4a).
Data collection included quantitative measurements (torque, Periotest values) and qualitative assessments (patient-reported outcome measures focusing on comfort, aesthetics, and functionality).
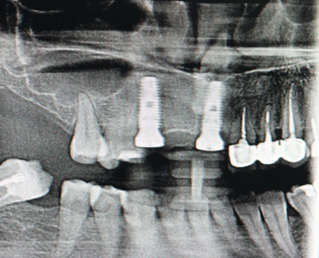 | 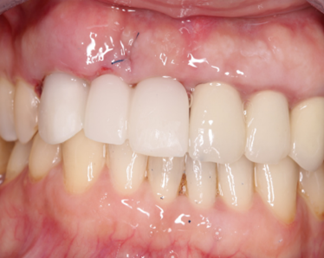 |
Fig. 3 After surgery photo. A. Radiological evaluation after implant placement. B. Fixation of immediate provisional crowns . | |
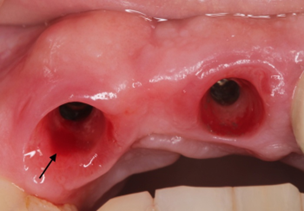 | 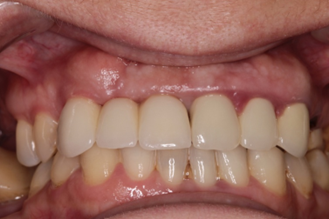 |
Fig. 4 Implant evaluation after osseointegration period. A. Soft tissue appearance and bleeding evaluation by Mombelli after osseointegration. B. Fixation of final work, and emergency profile evaluation. | |
Results
-Primary Stability:
Insertion torque exceeded the recommended threshold of 35 Ncm, ensuring immediate loading feasibility.
Periotest values of -5 and -6 corroborated excellent primary stability and osseointegration potential.
- Aesthetic and Functional Outcomes:
Gingival contours were preserved throughout the treatment period, with no signs of soft tissue recession or inflammation.
Provisional restorations provided satisfactory aesthetics, meeting patient expectations for anterior zone rehabilitation.
-Patient Satisfaction:
Post-treatment surveys indicated 85% satisfaction with comfort and appearance. The remaining 15% expressed mild concerns regarding initial adaptation to the provisional restorations, which were resolved within two weeks.
Literature reviews supported these findings, with success rates for immediate loading reported at 94-98%. Biomechanical studies emphasized maintaining occlusal forces below 150 Newtons to prevent micromovements during healing. Follow-up evaluations at 12 months confirmed implant stability, with repeated Periotest measurements remaining consistent.
According to postextraction implantation requirements, the implants were applied subcortically, to have enough space for the soft tissues. After the healing period, according to the measurements on the radiological image, we observed an insignificant bone remodeling with bone loss of 0.8 mm from the mesial and 0.7 mm from the distal. The platform of the implants being below the crestal level anyway, which demonstrates the effectiveness of the treatment method.
Discussion
Immediate loading minimizes treatment time while maintaining patient comfort and aesthetics. Atraumatic extraction techniques are pivotal in preserving alveolar bone integrity, particularly the vestibular plate, which is essential for achieving optimal aesthetic results. Temporary crowns play a crucial role in maintaining gingival contours and facilitating soft tissue adaptation [9].
The case study emphasizes the importance of achieving primary stability and avoiding lateral occlusal forces during the healing period. Statistical data support the protocol’s predictability, aligning with broader findings in contemporary literature [3, 6]. Challenges, such as patient-specific anatomical variability and bone density, underscore the need for tailored approaches.
Future research should explore advanced implant materials, surface modifications, and digital planning techniques to enhance outcomes further. The integration of these advancements could address current limitations and improve the predictability of immediate loading protocols.
Conclusions
Immediate loading of dental implants is a reliable and effective treatment method that reduces treatment time, ensures psychological comfort, and delivers stable, long-term results. Adherence to atraumatic techniques, precise implant placement, and meticulous soft tissue management is essential for success. This case study validates the protocol’s predictability and highlights its role in advancing patient care.
Competing interests
None declared.
Acknowledgements and funding
No external funding.
Ethics approval
Not needed for this study.
Informed consent for publication
Obtained.
Provenance and peer review
Not commissioned, externally peer review.
Author’s ORCID ID
Adrian Zgîrcea – https://orcid.org/0009-0000-9630-8656
References
- Albrektsson T, Branemark PI, Hansson HA, Lindström J. Osseointegrated titanium implants. Requirements for ensuring long-lasting direct bone-to-implant anchorage in humans. Acta Orthop Scand. 1981;52(2):155-170. doi: 10.3109/17453678108991776.
- Barzilay I. Immediate implants: their current status. Int J Prosthodont. 1993;6(2):169-175.
- Chele N. Implantarea imediată: riscuri și beneficii. Studiu preliminar [Immediate implantation: risks and benefits. Preliminary study]. Medicina Stomatologică. 2014;(3):56-64. Romanian.
- Chele N. Factorii determinanţi ai osteointegrării în implantologie [Osseointegation deteminant factors in implantology]. Medicina Stomatologică. 2015;(3):29-32. Romanian.
- Chele N, Motelica G, Zănoagă O, Slabari E. Extracţia dentară – tehnici, accidente şi complicaţii [Tooth extraction – techniques, accidents, and complications]. Chișinău: [s. n.]; 2022. 144 p. Romanian.
- Chele N, Topalo V, Sîrbu D. Instalarea imediată ghidată a implantelor dentare de stadiul doi [Guided immediate installation for stage two dental implants]. Medicina Stomatologică. 2015;(2):33-38. Romanian.
- Mostovei A. [Evaluation of the integration of endosseous dental implants installed in one session through flapless surgery] [dissertation]. Chișinău: Nicolae Testemitanu State University of Medicine and Pharmacy; 2014. 141 p. Romanian.
- Mostovei A. Formarea spațiului biologic periimplantar în tehnica flapless în dependență de tipul mucoasei [The biological width formation related to flapless technique and gingival biotype]. Bul Acad Sci Mold. 2013;(3):180-184. Romanian.
- Mostovei A, Topalo V, Chele N, et al. One-step vs. two-step early flapless placement of two-stage dental implants. Clin Oral Implant Res. 2013;24(Suppl 9):139-140.

