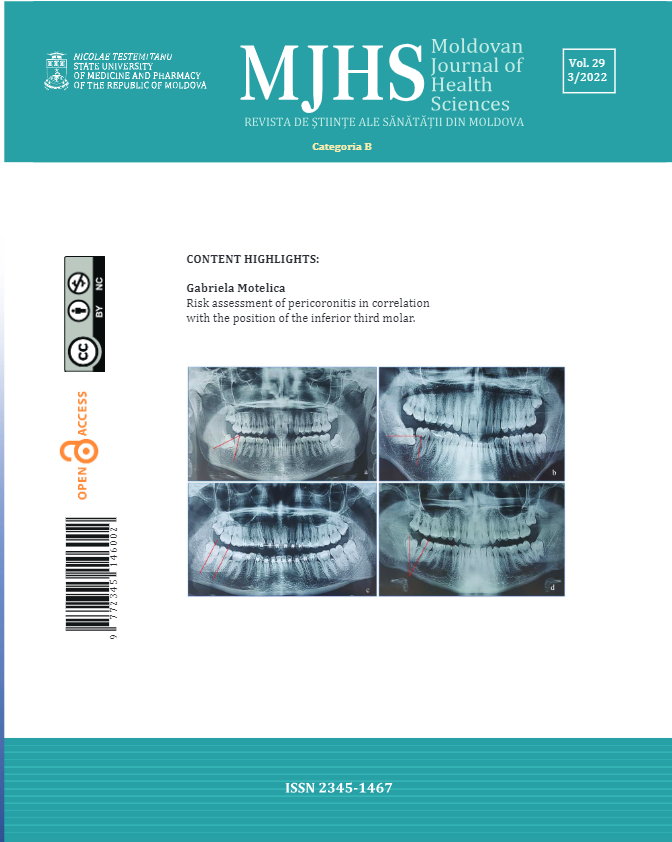
Changes of oxidative stress indices and antioxidant system in the liver tissue on the administration of some coordination compound of copper, derivatives of thiosemicarbazide
https://doi.org/10.52645/MJHS.2022.3.02
Introduction
Identification, study and testing of new remedies for treatment approaches of diseases, resulting from imbalance between oxidants and antioxidants in favor of oxidants, with potentially destructive potential and pathogenesis in liver disorders is of particular interest due to the increase in incidence and severity of these pathologies.
Material and methods
The action of novel local copper coordination compounds, thiosemicarbazide derivatives - CMD-4, CMJ-33 and CMT-67, was evaluated in experiments on white rats after subcutaneous administration in two different doses (0.1 and 1.0 µM / kg) 3 times a week for 30 days. The main indices of oxidative stress were evaluated: the level of malonic dialdehyde (MDA), nitric oxide derivatives (NO), S-nitrosothiols, advanced glycation end products (AGEs), advanced oxidation protein products (AOPP) and ischemia-modified proteins (IMP), and antioxidant system: - superoxidismutase (SOD) and catalase activity (CAT), the level of histidine (His) and total antioxidant activity (TAA) in liver tissue of white rats.
Results
The administration of CC resulted in the reduction of oxidative stress indices - MDA, AGEs and S-nitrosothiols, which denotes the antioxidant effect of the studied compounds. The level of NO and AOPP derivatives does not change substantially. When administering CMD-4 (1 µM / kg), SOD activity and catalase function decreased markedly. Changes in the content of His and TAA have been shown to be inconclusive, maintaining within the limits of the values recorded in the control group.
Conclusions
The elucidation of the modifications of the free radicals processes in liver tissues, which are the basis of the CC action, broadens the theoretical knowledge about the biological properties of a number of chemical compounds; as well provide new possibilities to explore perspective objects in order to obtain new efficient drug preparations.