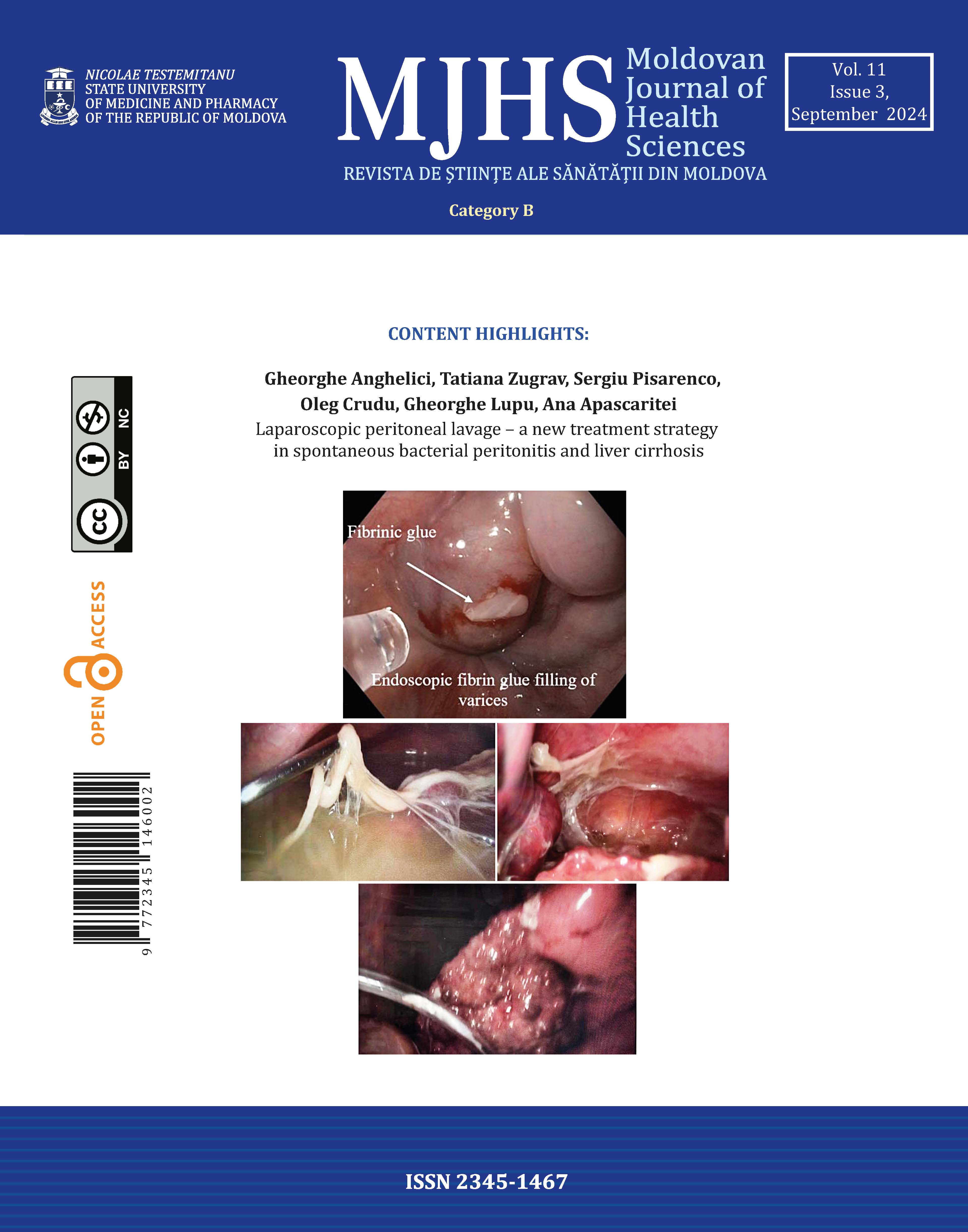
Laparoscopic peritoneal lavage – a new treatment strategy in spontaneous bacterial peritonitis and liver cirrhosis
https://doi.org/10.52645/MJHS.2024.3.01
Introduction
Bacterial infections in cirrhotic patients represent a major clinical problem, occuring 4-5 times more frequently compared to the general population and increasing mortality by leading to acute on chronic liver failure, subsequent decompensation, and multiorgan failure. The study’s purpose is to determine the possibilities of laparoscopy in the treatment of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis with decompensated liver cirrhosis.
Materials and methods
A retrospective descriptive study was conducted on 82 patients diagnosed with liver cirrhosis and spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, who were admitted to the Constantin Tibirna Surgery department No2, Holy Trinity Municipal Clinical Hospital and the Scientific Research Laboratory of Hepatic Surgery, Nicolae Testemițanu State University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Chisinau, Republic of Moldova, between January 2012 and December 2021. Patients who underwent surgical drainage of the abdominal cavity by laparoscopy with postoperative peritoneal lavage with antibiotics were selected. All patients received standard treatment for the correction of liver function and complications of portal hypertension. The data were extracted from the medical records of the hospital archive, and the patient database was compiled. Data analysis was performed using simple statistical calculations.
Results
Positive ascitic fluid bacterial culture was in 29.2% (24 patients), while 70.7% (58 patients) had culture-negative ascites and peritonitis. The most frequent bacterial species was E. coli, present in 54.1% (13 patients). Mortality was 8.5% (7 patients) due to progressive liver failure. Recurrence of ascites and peritonitis at 1 month was 6.0% (5 patients).
Conclusions
The laparoscopic approach in spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in patients with decompensated liver cirrhosis allows for better sanitation of the abdominal cavity, improves peritoneal absorption, and deserves establishment as clinical practice for patients with ascites and peritonitis and cirrhosis.