Variability of urodynamic parameters in patients with idiopathic overactive bladder before intradetrusor botulinum toxin injections
https://doi.org/10.52645/MJHS.2022.2.01
Introduction
The aim of study was to establish if the treatment of overactive bladder in women and its result reported by patients were different depending on the findings of urodynamics, performed before botulinum toxin injection. We obtained clinical data based on the necessity and importance of performing urodynamic tests up to surgical treatment with botulinum toxin A injection in detrusor muscle, at patients diagnosed with idiopathic overactive bladder and detrusor overactivity, offering a guarantee of an effective and long-lasting treatment and assure with predictive parameters for some postoperative complications.
Material and methods
The research was carried out at the Department of Urology and Surgical Nephrology, during the years 2019 – 2022. After applying the inclusion and exclusion criteria, 36 women diagnosed with overactive bladder were enrolled in the prospective pilot study, aged between 18 and 70 years, refractory to drug treatment and investigated urodynamic by excluding/including the presence of detrusor overactivity and clinically using voiding diary/24h, bladder symptoms and Quality of Life questionnaires before and after botulinum toxin A injection. The primary data were analyzed and presented as a mean and standard deviation.
Results
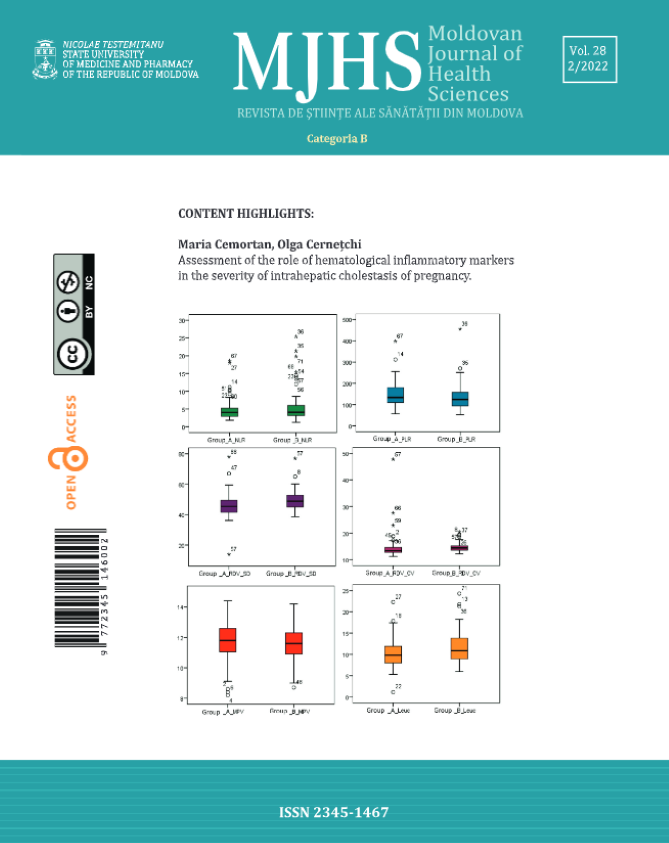
All women involved in the study were diagnosed clinically and urodynamic with overactive bladder, of which 55.5% of cases were associated with detrusor overactivity and subsequently received BTX-A injectable surgical treatment with a dose of 100U. At urodynamics, the low values of the indices obtained at cystometry were established: first sensation of bladder filling (79.8±56.3 ml), first desire to void (117.8±103.2 ml), strong desire to void (162±125 ml) and maximal cystometric capacity (183.4±139.8 ml), which correlated in 100% cases with OAB symptoms (urinary urgency, frequency and nocturia) from the OABSS validated questionnaire. The capacity of the bladder at each sensation was lower, being inversely proportional to the detrusor overactivity present in women with OAB. Based on UDS data, the diagnosis of OABi with detrusor overactivity was confirmed by establishing the presence of phasic detrusor contractions (3.9±1.1), increased values of detrusor pressure (45.9±23.9 cmH2O) and the presence of bladder hypocompliance (10.6±11.5 ml/cmH2O), these data in 100% of cases predicted an effective BTX-A injection. Daily activity and psychosocial behavior improved after intradetrusor botulinum injections toxin was influenced by reducing daytime urination from 28% to 40% and urinary urgency from 30 to 69%.
Conclusions
This study identified a number of statistically significant urodynamic variables associated with objective clinical data, which confirm the impact of severity of idiopathic overactive bladder symptoms and the subsequent effect of botulinum toxin type A injections in case of urodynamic confirmation of detrusor overactivity presence.