The influence of diabetes mellitus on blood vessels amount in case of breast cancer
https://doi.org/10.52645/MJHS.2023.1.01
Introduction
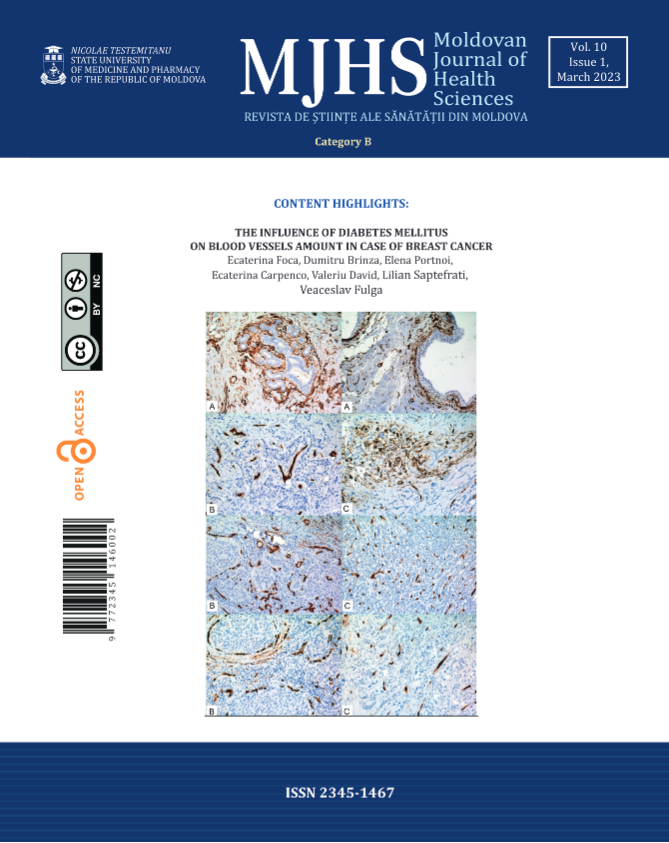
Breast cancer is one of the most common cancers in females worldwide. There are evidences that women with diabetes mellitus have a 40% higher risk of mortality. CD34 is a cell surface glycoprotein, which functions as a cell-cell adhesion factor. Although its expression is traditionally related to hematopoietic cells, it is actually found on many other types of cells, endothelial too. Nowadays there are evidences that CD34 is a prognostic indicator by emphasizing its low expression in malignant tumors compared to benign ones. The aim of study was to determine the presence and numerical distribution of CD34+ vessels in the normal mammary gland, as well as in NST breast carcinomas, with and without diabetes mellitus type 2.
Materials and methods
We processed immunohistochemically 58 invasive breast carcinomas of NST type. In 29 of cases, tumors were associated with diabetes.
Results
The present study did not reveal any statistical and morphological differences in CD34 expression between compared groups.
Conclusions
The expression of CD34 in breast cancer stroma is not homogenous, irrespective of association with diabetes mellitus type 2. The question if breast carcinoma and diabetes mellitus are concurrent or associated disorders remains open. Probably, the effect of carcinoma prevails in influencing the structure of the tumor microenvironment. We expect a further confirmation in larger study groups.